Keeping abreast of the latest trends and events in the global technology ecosystem is crucial for improving and expanding the space, as these trends provide insights that inspire further investments and adoption.
To this end, global management consulting firm, McKinsey & Company has carefully studied and compared the activities of various trends across diverse sub-sectors of technology. The results of this research are explained in a report of 14 great trends that cause the largest waves in the world; as well as their projected potential to further disrupt the global digital economy in the coming years.
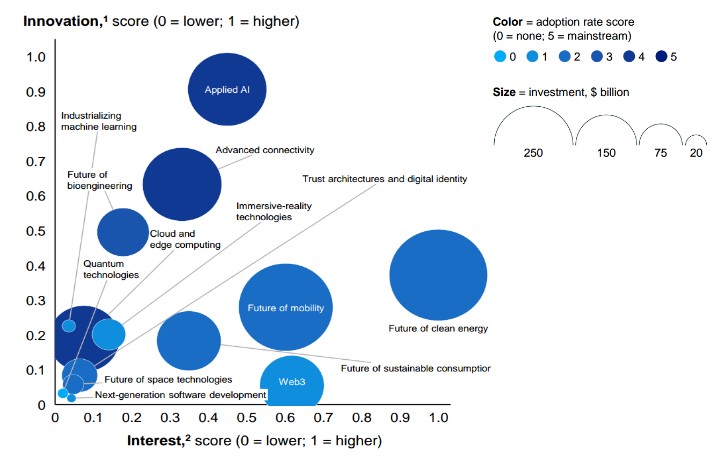
The Top 14 Technology Trends
• Applied AI: Applied AI has the highest innovation score of all 14 trends. Worth about 10 to 15 trillion dollars, the industry is looking to revolutionize technology and the way it interacts with human existence.
In 2021, AI-related companies attracted $93.5 billion in private investment, as well as a 30× growth in the relative number of patents filed in the same year.
Also, training speeds have improved by 94.4% since 2018.For developing countries like Nigeria, the prospects of AI are infinite. It can transform almost every sector of the country’s economy as it has proven to be useful in risk management, service operations optimization, product and service development, etc.
• Advanced Connectivity: More people are getting connected to the internet through advanced technologies. These technologies include Optical fibre, Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) networks, Wifi 6, 5G cellular and Low-Earth Orbit Satellite Constellations.
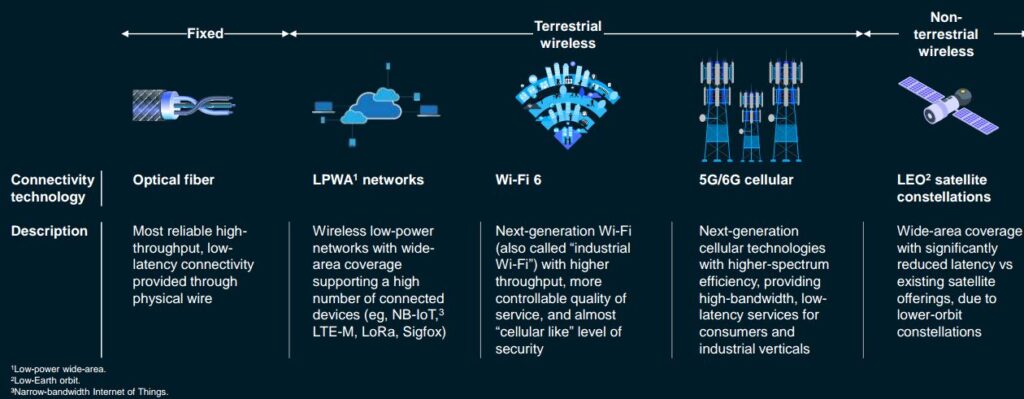
One of the most significant features of the trend is that it has seen an overall 10-20% revenue increase globally. While 2021 welcomed around 300 million newcomers to the internet to make a total of 4.9 billion users worldwide, the numbers are expected to rise to an estimated 51.9 billion connected devices by 2025.
This trend will have a great impact on almost every industry as it is key to unlocking many more potentials in IoT applications, mobile augmented reality (AR)/virtual reality (VR) and cloud computing, among others.
• Cloud and Edge Computing:
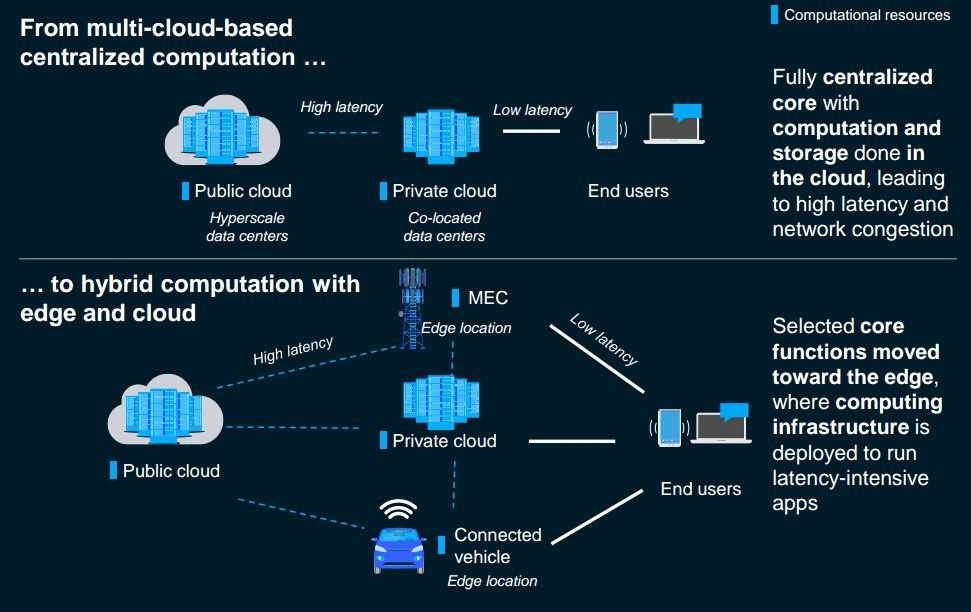
From being a private and/or public enterprise to being a hybrid technology with 80% of cloud users using the hybrid mix. Edge computing has grown to provide organizations with data sovereignty, autonomy, better security and latency.
About $250 billion is projected to be spent globally on edge computing by 2025 as over 26% of servers shipped in 2024 will be deployed at the edge.
• Web3: The democratization of the internet has been a long-trending development in the global tech space. The recent buzz in the Web3 space is its laudable contribution to the gaming industry where it has presented a new paradigm for the industry’s revenue models. From Pay to Play (P2P) and Free to Play (F2P) models previously known, as the Play and Earn (P&E) model that is rocking the industry worldwide.
2021 saw a total of over 34,000 active web developers grace the global stage. This is majorly attributed to the steady increase in access and participation in the trend over the years.
The most dominant web3 applications have been Defi, digital art, gaming and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
• Immersive-Reality Technologies: As new as they are in practicality, Immersive-Reality technologies have been a well-anticipated trend to man since the dawn of futuristic movies.
In the last couple of years, these technologies have amassed so much fame and interest with about $3.9 billion contributed by Venture Capitals (VCs) to fund VR and AR startups in 2021. From 2018 to 2021, the number of patents filed by companies running immersive reality technologies has also experienced a 2× growth rate.
By 2035, it is projected that the industry’s market size will increase to about $1.2 trillion, as well as a 66% CAGR in enterprise adoption of AR through 2026.
• Future of Bioengineering: Despite being a nascent subject in Nigeria and most developing countries, Bioengineering has been making the rounds in developed countries. The three major areas of focus in the technology are biomolecules, biosystems, machine interfaces and biocomputing.
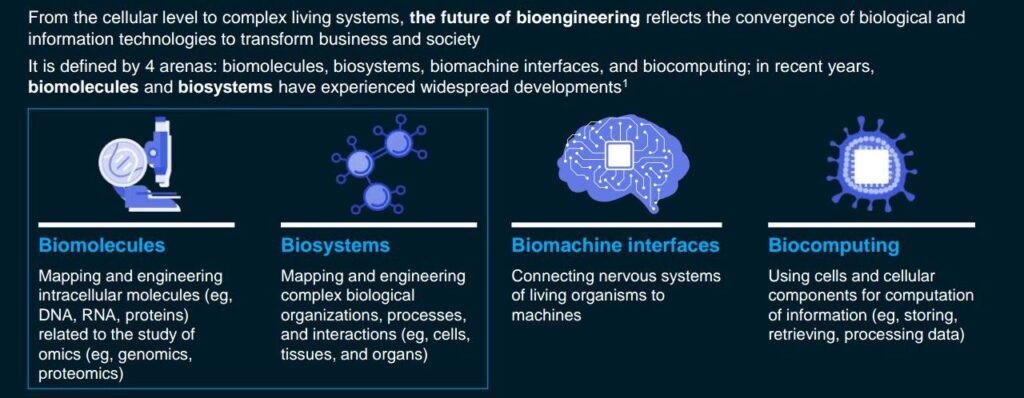
Across industries, efforts in developing the adoption of bio-related technology are increasing on a global scale. About 400 feasible use cases have been identified in this regard.
The technology is invested in enhancing sustainability, reducing cost and global carbon footprints as well as providing renewable resources.
• Future of Clean Energy: The growing concern for climate change has inspired a thriving trend around providing energy solutions to help achieve net-zero emissions in the not-so-distant future. These trends revolve around power storage, power distribution and smart grid systems.
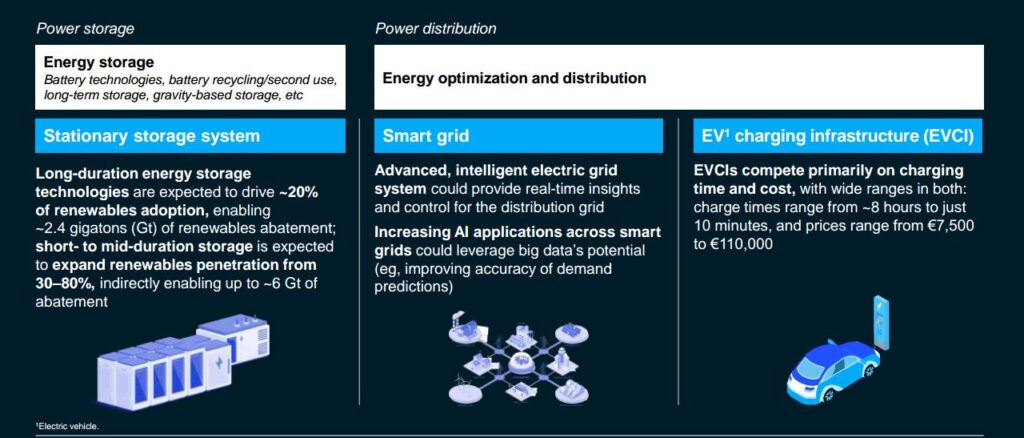
Consequently, approximately 84% of global power demand which is estimated to grow 3× by 2050, can be met using renewable energy.
At this rate, there should be a 30-60% decrease in the price of batteries by 2030 and 2035 as well as a 3.3× growth in sustainable fuel distribution, globally.
2050 is further poised to be a good year for carbon abatement as 80-90% of the global energy mix will be sourced from renewable energy, abating 2.5 gigatons of carbon.
• Future of Mobility: Mobility is currently undergoing its “second great inflexion point” as a result of its transition toward an autonomous, connected, electric and smart (ACES) future.
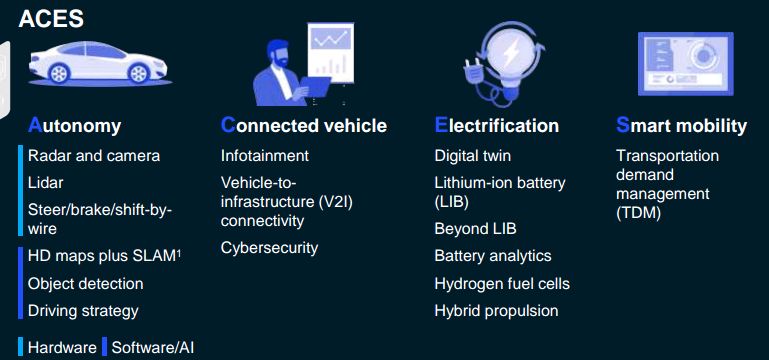
While its major impact has been on the automotive and assembly sector, a handful of other sectors and industries are sure to be disrupted by the trend as it is committed to cost-effectiveness, efficiency and sustainability of land and air transportation of people and goods.
By 2030, 50% of miles travelled are expected to be done with shared transportation modes as well as a 1:1 cost parity for small Electric Vehicles (EV) with Internal Combustion engines (ICE) and fuel parity.
• Future of Sustainable Consumption: Low carbon; waste conscious; reduce, reuse, recycle; biobased; biodegradable and nontoxic—these are the patterns that reflect enhancements in conscious consumption.
According to the McKinsey report, 80% of millennials want to work for a company that is strong on sustainability and other environmental, social and governance (ESG) dimensions. Also, a 50% growth rate has been recorded in sustainable brands as opposed to others.
Nonetheless, 90% emission reduction, paired with wholesome emission removal, is required to avoid an environmental crisis. This will create a $4-6 trillion addressable market focused on industrial and individual end-use by 2030.
• Trust Architecture and Digital Identity:
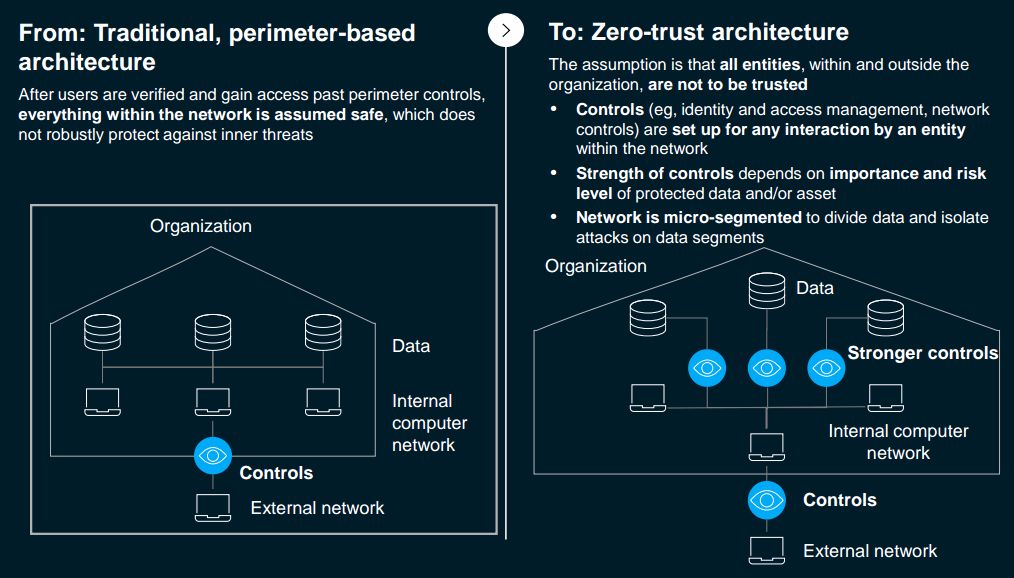
The high rate of cyberattacks and cyber regulations and policies across borders are the factors that gave rise to this trend. Digital trust, therefore, addresses the digital risks across data, cloud, AI and analytics and risk culture.
Some noteworthy technologies that have sprung up under the trust Architecture and digital identity sub-sector are zero-trust architecture, self-sovereign identity (SSI), privacy engineering, “passwordless” identity, and explainable AI.
These technological advancements are therefore poised to reduce cyber threats and risks, as well as their negative impacts on consumers and the tech ecosystem at large.
• Future of Space Technologies:
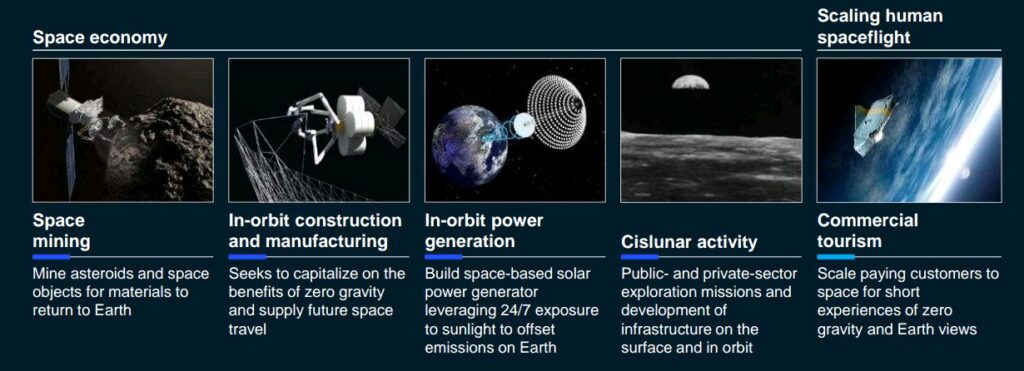
The largest shift in space in the past 5 years, according to the report, has been the acceleration down the cost curve which is increasingly unlocking new capabilities.
Today, the estimated value of space technologies in the world is about $447 billion. This value is, however, projected to grow over 10% by 2030.
Furthermore, participation in the industry has increased with 600+ companies (governments and startups) recorded to be involved in the space industry.
• Industrializing Machine Learning:
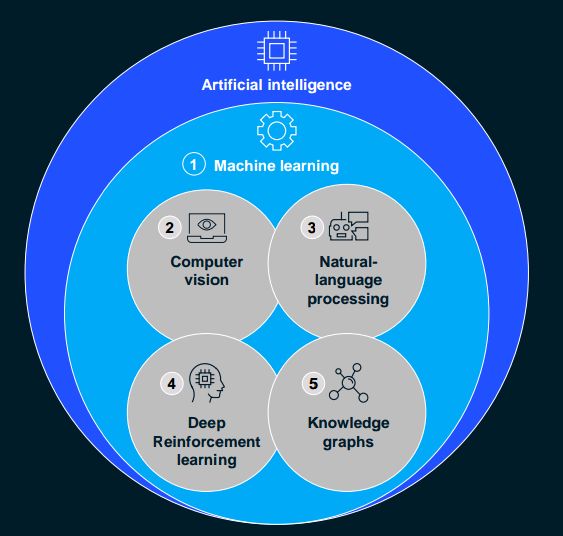
Machine learning (ML) has been ascribed the potential to reduce the time between proof of concept to production by about 8-10×. It also guarantees approximately 60% less value erosion time 12 months from model deployment because of living model operations. Its workflows are the processes that bring AI and ML into production for real-world use.
By adopting this technology, governments, people and industries can have access to more efficient product prototyping and testing; improve quality assurance, engage customers, allow users to develop hands-on training, and introduce new products and services, among other things. However, to unlock scalability, the cost of ML technology will need to be reduced by over 50%.
• Next-Generation Software Development: Low-code and no-code platforms, infrastructure-as-code, microservices and APIs, AI “pair programmer”, AI-based testing, and automated code review are the most notable technologies in this trend.ThearThesere technologies that are designed to facilitate greater participation of “citizen developers” in every society.
By 2025, the share of new application development that will leverage low-code is about 70% as the market size for software development will also increase by at least 21%, reaching approximately $600 million by 2026. There will also be a massive reduction in the development time of applications as well as a less than 1 day resolution time for configuration issues.
• Quantum Technologies: Although this trend has been in existence for a long time, it is the activities of a few technologies under it that have attracted observers’ attention.

Valued at about $300-700 billion, quantum technologies are capable of disrupting the automotive, chemicals, finance and pharmaceutical industries greatly.
The estimated timeline to unlock several of the currently identified use cases of these technologies is less than 10 years. However, observers are optimistic that if and when this technology matures and scales up, it will unleash significant business value across industries.

































